
Oracle creates server processes to handle requests from connected user processes. Oracle processes are invoked by other processes to perform functions on behalf of the invoking process. User processes also manage communication with the server process through the program interface, which is described in a later section. User processes are created and maintained to run the software code of an application program (such as an OCI or OCCI program) or an Oracle tool (such as Enterprise Manager). A process generally has its own private memory area in which it runs.Īn Oracle database server has two general types of processes: user processes and Oracle processes. Some operating systems use the terms job or task.
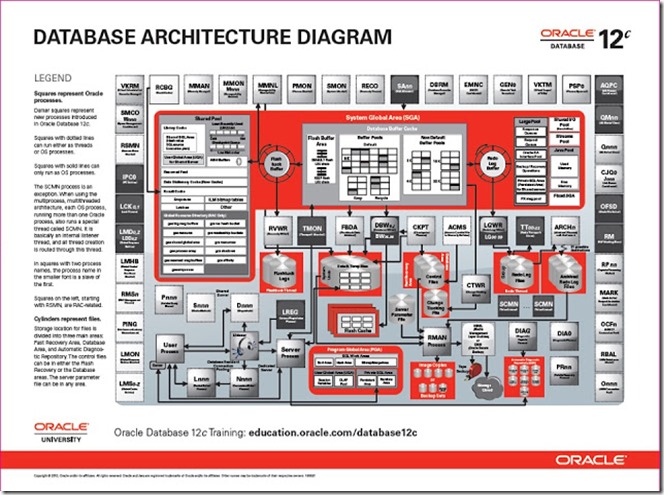
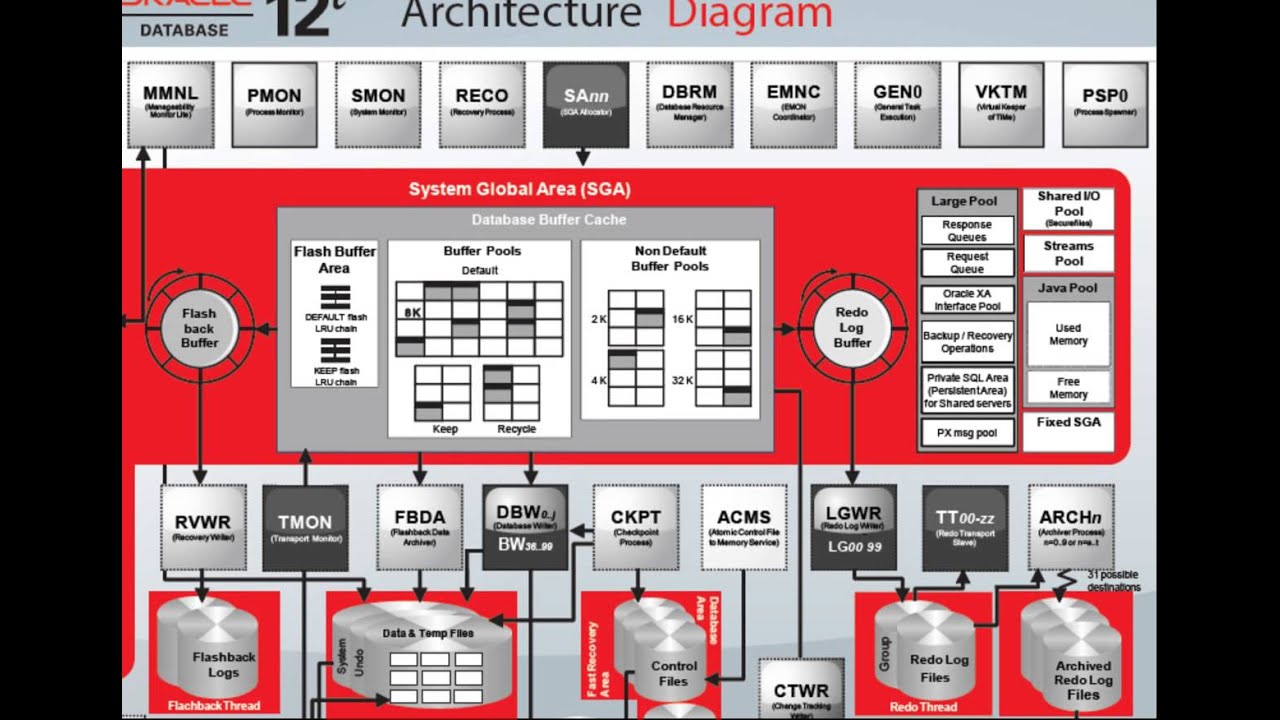
> Overview of Parameter File, Server Parameter File & Password fileĪ process is a "thread of control" or a mechanism in an operating system that can run a series of steps. > Overview of Physical & logical Database Structures In this section, will cover the following topics related to the Oracle architecture: An instance consists of some memory structures and the background processes, whereas a database refers to the disk resources. Oracle Database 11g Architectureīasically, there are two main components of Oracle database –– instance and database itself. Because the physical and logical structures are separate, the physical storage of data can be managed without affecting the access to logical storage structures. The database has logical structures and physical structures. There is no need for peak workloads, because capacity can be easily added or reallocated from the resource pools as needed. With this architecture, each new system can be rapidly provisioned from the pool of components. Enterprise grid computing creates large pools of industry-standard, modular storage and servers.

Oracle Database is the first database designed for enterprise grid computing, the most flexible and cost effective way to manage information and applications. A database server also prevents unauthorized access and provides efficient solutions for failure recovery. In general, a server reliably manages a large amount of data in a multiuser environment so that many users can concurrently access the same data. A database server is the key to information management.
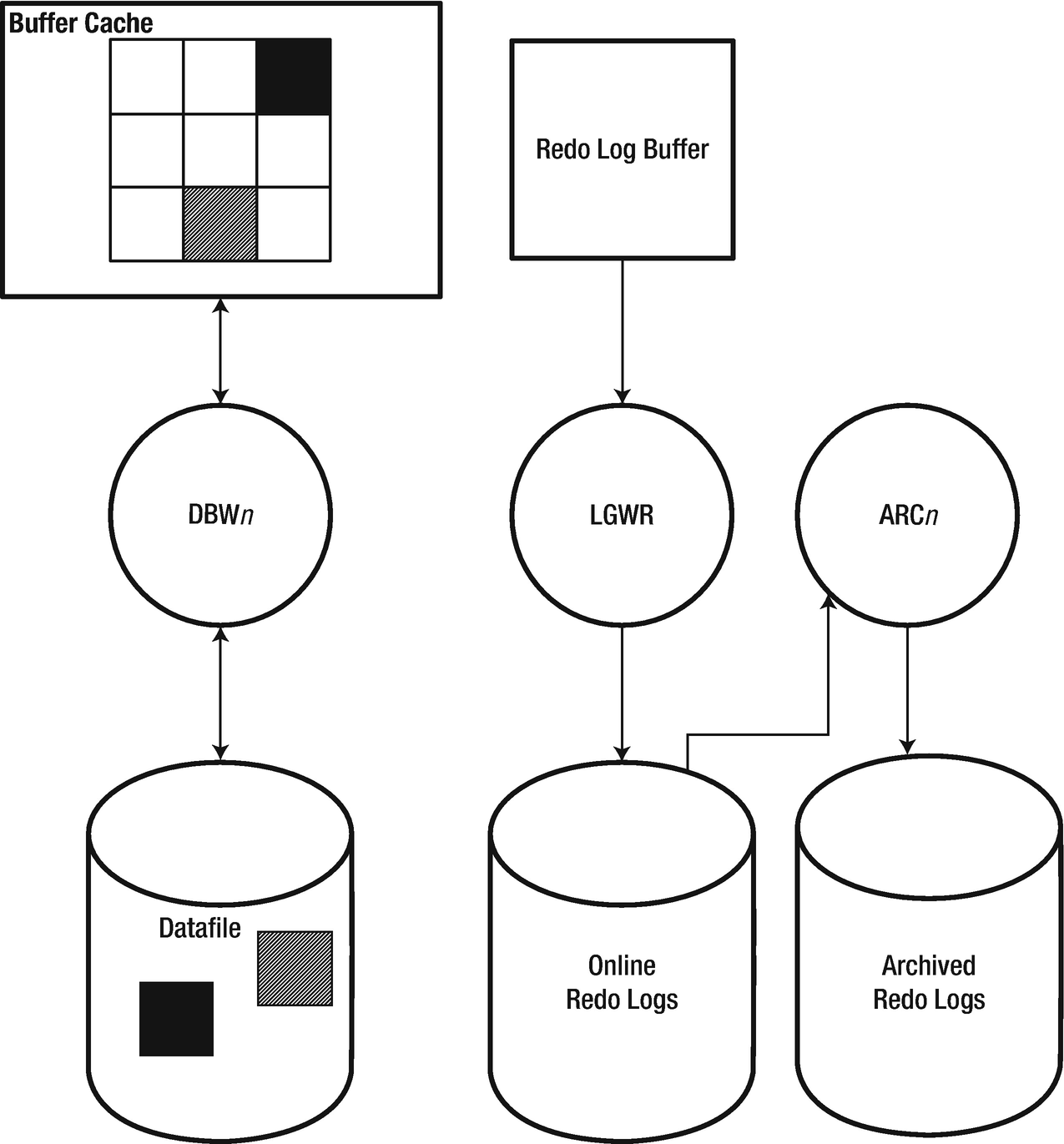
The purpose of a database is to store and retrieve related information.
A database is a collection of data treated as a unit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
